Giới thiệu
The landscape of search is undergoing a profound transformation, moving beyond traditional keyword matching to embrace AI-powered generative answers. This evolution presents a significant challenge for SEO professionals, as content must now be structured not just for crawlers, but for advanced language models capable of understanding context and intent. Merely optimizing for traditional ranking factors is no longer sufficient to secure visibility in these intelligent search environments. This article delves into technical SEO for GEO, providing actionable strategies to adapt your website's infrastructure. It will demonstrate how to architect your site to facilitate AI discovery, enhance content comprehension, and ultimately, ensure your valuable information is effectively utilized by generative engines. For a comprehensive overview, see Generative Engine Optimization.
The Evolution of Search: Why Technical Foundations Matter for GEO
The search landscape has fundamentally transformed, moving beyond traditional "ten blue links" to Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), where AI models synthesize answers directly. This pivotal shift necessitates a re-evaluation of how websites present information.
Technical SEO now serves as the indispensable "translator," bridging the gap between intricate website architectures and the sophisticated comprehension abilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). These AI engines do not merely crawl links; they parse context, intent, and relationships.
Therefore, they inherently prioritize websites built upon robust, structured, and high-performance technical foundations. Such environments enable LLMs to accurately interpret data, ensuring content is reliably discovered, understood, and leveraged to formulate precise, authoritative AI-generated responses, thereby driving enhanced visibility in the evolving search paradigm.
Facilitating AI Discovery: Crawlability and Indexing for LLMs
Crawlability remains foundational for Generative Engine Optimization, but with a refined focus on AI's unique needs. Robots.txt files require meticulous review to ensure emerging AI user-agents—which may differ from traditional search engine bots—are granted appropriate access to valuable content while explicitly restricting irrelevant or low-quality pages. Concurrently, XML sitemaps become critical navigational guides, explicitly directing AI crawlers to your most authoritative, structured, and context-rich content, ensuring comprehensive discovery by generative models.
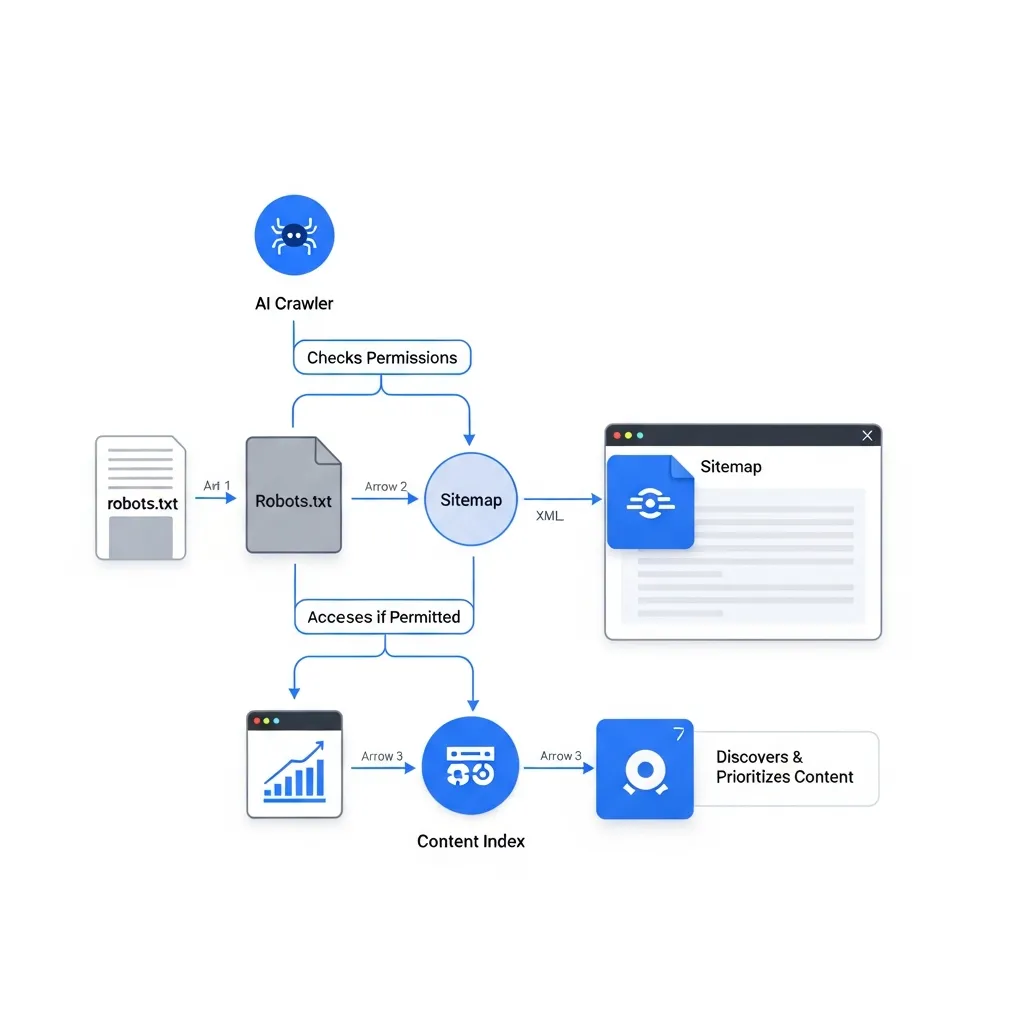
Effective crawl budget management is paramount to ensure AI bots prioritize high-value content. Strategically direct these bots toward pages offering deep, factual answers or unique insights, which are most likely to be featured in AI-generated responses. Regularly analyzing log files is crucial for this validation. By tracking specific AI user-agent activity, SEO professionals can verify crawl patterns, identify overlooked sections, and iteratively refine directives to optimize technical SEO for GEO results.
Advanced Structured Data: Providing Explicit Context for Generative Engines
Advanced structured data serves as the Rosetta Stone for generative engines, providing explicit, machine-readable context that significantly enhances their ability to understand, process, and ultimately cite your content. While traditional SEO uses Schema Markup for rich snippets, GEO elevates its purpose to defining intricate entities and their relationships, ensuring AI models grasp the nuanced meaning behind your information.
Implementing comprehensive Schema Markup (JSON-LD) is paramount. This involves going beyond basic Article or Product schema to fully articulate the "who, what, when, where, and why" of your content. Generative engines thrive on clear entity definitions, making properties like name, description, url, and sameAs critical for establishing authority and disambiguation.
Deepening AI Understanding with Specific Schema Types
To foster superior AI clarity, leverage specific schema types and properties that directly inform generative models about content intent and relationships:
- The
Aboutproperty: Explicitly links a piece of content to a particular topic or entity, signaling to AI what the page is fundamentally about. - The
Mentionsproperty: Highlights other significant entities discussed within the content, even if they aren't the primary focus. - The
Speakableproperty: Invaluable for voice search or AI-generated summaries, indicating which parts of an article are suitable for audible rendering.
Mapping content clusters becomes more effective through HasPart and IsPartOf properties. These allow you to define hierarchical and associative relationships between different articles, sections, or even entire sub-domains. By explicitly stating that an article IsPartOf a broader Series or that a WebPage HasPart sections, you build a robust knowledge graph that guides AI through your topical authority.
The GEO Schema Blueprint
For high-impact GEO schema implementation, follow this structured approach:
- Identify Core Entities: Determine the primary subjects, organizations, people, and concepts your content discusses.
- Map Relationships: Define how these entities relate to each other and to your content.
- Implement Advanced Schema Types: Utilize
About,Mentions,Speakable,Author,Publisher, and other relevant properties. - Connect Content Clusters: Employ
HasPartandIsPartOfto establish semantic links between related pages. - Validate and Monitor: Use Schema Markup Validators and rich results tests to ensure correct implementation.
Practical Code Example for GEO
Here’s a simplified JSON-LD snippet demonstrating how to explicitly define relationships and entities for a news article:
The correlation between rich snippets and AI citation frequency is direct. When structured data is correctly implemented, it enables search engines to display rich results, which are more prominent and informative. For generative engines, this explicit, unambiguous data acts as a highly reliable source. AI models are more likely to extract and cite information that is clearly defined, increasing the likelihood of your content appearing in AI-generated answers.
Architecting for Authority: Internal Linking and Topical Clusters
Architecting for AI-powered search demands a deliberate approach to internal linking that extends beyond traditional SEO signals. A flat site structure is crucial, minimizing click depth to facilitate efficient discovery by AI bots and ensure all relevant content is easily accessible. This structure enables generative engines to quickly map your informational landscape.
Moreover, semantic internal linking becomes a powerful tool for signaling topical relevance and hierarchy. By creating interconnected topical clusters, you explicitly guide LLMs through your domain expertise, helping them understand the depth and breadth of your content. The strategic use of descriptive anchor text is equally vital; it provides direct signals to LLMs regarding the precise relationship and subject matter of linked pages, bolstering your site's perceived authority and aiding accurate content synthesis.
Performance as a GEO Signal: Speed and Mobile Readiness
Performance metrics are increasingly pivotal for technical SEO for GEO, signaling content quality and reliability to AI models. Core Web Vitals (CWV) directly influence how AI prioritizes content, as a superior user experience translates to higher confidence for generative engines. Poor CWV scores can indicate a suboptimal experience, potentially leading AI to deprioritize your content in favor of faster sources.
A mobile-first infrastructure is non-negotiable, ensuring AI models seamlessly interpret and synthesize information from responsive designs without encountering rendering issues. Furthermore, reducing server response times (Time to First Byte – TTFB) is critical. Faster TTFB enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to ingest data more efficiently, significantly improving the likelihood of your content being featured in AI-generated answers by presenting a readily accessible and performant source.
Strategic Insights: Avoiding Common Technical GEO Mistakes
While advanced structured data is crucial, over-optimizing schema is a significant pitfall. Excessive or misleading markup can confuse generative models, leading to misinterpretations rather than enhanced understanding, and risks manual penalties. A common mistake is attempting to mark up every minute detail, which often leads to inaccurate entity relationships. Instead, focus on providing clear, relevant context.
Furthermore, content freshness signals are paramount for AI-powered search. Unlike traditional search, which might rank older, authoritative content, AI engines often prioritize the latest, most accurate information for generative answers. Additionally, sites heavily reliant on client-side JavaScript for critical content often present ingestion challenges. Server-side rendering or hybrid approaches are currently more robust for ensuring AI discovery and accurate context interpretation.
Traditional Technical SEO vs. GEO: Key Differences
GEO marks a profound shift in methodology. We are moving from keyword density to deep entity-based optimization, as AI understands concepts rather than just strings of text. Citation-readiness is now paramount, often superseding traditional ranking positions. The technical SEO professional's role is evolving to architect content specifically for AI consumption, ensuring accurate attribution. A common mistake is underestimating explicit semantic signals, which hinders an AI's ability to confidently cite your content as a primary source.
Future-Proofing Your Technical Strategy for AI Search
Future-proofing demands prioritizing explicit semantic signals and structured data for AI comprehension. Continuous monitoring and adaptation are paramount; simply deploying schema once is insufficient. The future of technical SEO lies in proactively structuring information to ensure citation-readiness. This symbiotic relationship provides AI with reliable data, enriching the overall search experience. Avoid the common mistake of neglecting ongoing schema audits, which can lead to AI misinterpretations as models evolve. Embrace this dynamic evolution by auditing your current schema for AI readiness today.
Kết luận
Technical SEO for GEO demands a fundamental re-evaluation of website infrastructure to align with AI-powered search. This article has emphasized the importance of adapting technical practices—from advanced structured data and semantic architecture to performance optimization—to ensure content is accurately discovered and cited by generative engines. This proactive approach ensures your information is correctly interpreted and utilized. For SEO professionals, embracing these strategic technical adaptations is no longer optional; it is essential for maintaining visibility and establishing authority in the evolving search landscape. Begin auditing and refining your digital infrastructure now to future-proof your presence in AI-driven search.
FAQ
What is technical SEO for GEO?
Technical SEO for GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) refers to the practice of optimizing a website's technical infrastructure—such as schema markup, site speed, and crawlability—specifically to help AI models and generative engines discover, understand, and cite your content accurately.
How does structured data impact AI search results?
Structured data acts as a machine-readable guide for AI. By using JSON-LD to define entities and their relationships, you provide explicit context that allows generative engines to synthesize your information more reliably and increase the likelihood of your site being cited as a source.
Why are Core Web Vitals important for GEO?
Core Web Vitals are a proxy for user experience. AI models prioritize high-quality, reliable sources. A fast, responsive site (good CWV) signals to generative engines that your content is hosted on a stable and performant platform, making it a preferred source for AI-generated answers.
What is the difference between traditional SEO and GEO?
Traditional SEO focuses on ranking in the "ten blue links" through keyword matching and backlinks. GEO focuses on "citation-readiness" and entity-based optimization, ensuring that AI models can understand the context of your content well enough to include it in synthesized, generative responses.