The digital landscape is experiencing a seismic shift in how users discover and interact with information. For years, the search paradigm revolved around navigating lists of blue links on search engine results pages (SERPs). However, this model is rapidly evolving. Today, users increasingly turn to sophisticated generative AI models that synthesize vast amounts of data into direct answers, concise summaries, and engaging conversational responses. This transformation presents both unprecedented opportunities and significant challenges for businesses striving for organic visibility.
Traditional Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategies, while still foundational, are proving insufficient in this new environment. Optimizing solely for keyword rankings or click-through rates overlooks the fundamental change in how information is processed and consumed. As generative AI engines become a primary interface for user queries, content creators must ensure their work is not merely indexed, but also understood, interpreted, and accurately cited by these advanced systems. Without proactive adaptation, even high-quality, authoritative content may become functionally invisible, overshadowed by AI-generated responses that draw from sources better optimized for machine comprehension.
This comprehensive guide introduces Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), an essential evolution of SEO designed for the age of artificial intelligence. GEO moves beyond traditional ranking signals to focus on clarity, accuracy, and undeniable authority, ensuring content is trustworthy for large language models (LLMs). It is about securing a brand’s presence and ensuring its expertise is recognized and accurately represented within conversational search experiences.
Through this article, SEO professionals and marketing managers will gain actionable insights to integrate Generative Engine Optimization strategies into their existing digital marketing efforts. We will explore how to adapt content for optimal AI comprehension, establish unparalleled brand authority through E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness), and redefine success metrics in this dynamic new frontier.
The Evolution of Search: Understanding Generative Engine Optimization
The landscape of search is undergoing its most profound transformation since its inception. No longer limited to a list of links, search experiences increasingly feature AI-generated answers synthesized directly from multiple sources to provide immediate, comprehensive responses. This shift necessitates a new approach to digital visibility: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO).
GEO is the strategic discipline of optimizing digital content to be effectively understood and utilized by LLMs and other generative AI systems. It moves beyond traditional keyword rankings, focusing instead on how content can serve as a foundational, authoritative source for AI-driven engines.
For SEO professionals and marketing managers, staying current with this evolution is vital for maintaining organic visibility. As users increasingly interact with AI summaries, the pathways to discovery are diversifying. Failing to adapt means risking obscurity in a progressively AI-mediated search environment.
The core objective of GEO is to position your content as a primary, authoritative source that LLMs confidently draw upon when formulating responses. This means optimizing for clarity, accuracy, and comprehensiveness, ensuring your information is not just found, but also trusted and synthesized by AI.
Traditional SEO vs. Generative Engine Optimization: Key Differences
While the principles of user value and technical integrity remain crucial, generative AI has reshaped the search landscape, demanding a distinct strategic pivot. This is a paradigm change in how content achieves impact.
To navigate this shift effectively, it is helpful to analyze the core GEO vs traditional SEO distinctions.
From Keywords to Entities
Traditionally, SEO emphasized keyword density to signal relevance. However, generative engines operate on a deeper understanding of language; they comprehend concepts, relationships, and nuances. This necessitates a move toward entity-based context. Your content must thoroughly cover a topic by exploring all related entities—people, places, organizations, and abstract concepts—and their interconnections. It is about building a rich, semantic web of information that allows an AI to grasp the full depth of your subject matter.
In my experience at Planik.io, a common mistake is treating GEO as a mere extension of traditional SEO. For instance, one client initially focused on keyword stuffing for informational content. By shifting their strategy to explore related entities and provide structured answers, we observed a 30% increase in their content being referenced in AI summaries.
Beyond Backlinks: Citation Frequency and Relevance
While a robust backlink profile still signals authority, GEO introduces a new metric: citation frequency and relevance. Generative AI prioritizes content that serves as a definitive source. The goal is to create content so authoritative that AI models actively select and synthesize it into direct answers, explicitly citing your brand. This requires a focus on factual accuracy and unique insights that make your content indispensable.
CTR vs. Information Synthesis and Zero-Click Impact
Traditional SEO measures success through Click-Through Rates (CTR). With generative AI, the landscape includes zero-click solutions, where the AI answers the query without the user needing to click through. In GEO, success is about being the source from which the AI synthesizes its answer. If Planik.io content provides the perfect answer and the AI uses it, that is a GEO win, even without a click. This demands a strategic approach to content structure to ensure key information is easily extractable.
From Ranking to Being Cited
The most significant shift in GEO is the transition from “ranking” to “being cited.” Traditional SEO aims for a numerical position on a SERP. GEO aims for your content to be the foundational knowledge an AI uses to construct its response. The most effective approach is becoming the undeniable authority on a topic, creating content so well-structured that an AI model must cite it to provide a complete answer.
How Large Language Models and Generative Engines Process Information
Understanding how LLMs interpret and synthesize information is foundational to effective GEO. Unlike traditional engines that match keywords, generative engines aim to understand user intent and provide direct answers.
Central to this process is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). When a user submits a query, the engine retrieves relevant information from a vast index of data. This grounds the LLM’s response in factual data, mitigating the risk of “hallucinations.” Following retrieval, the LLM generates a coherent answer by synthesizing the most pertinent facts.
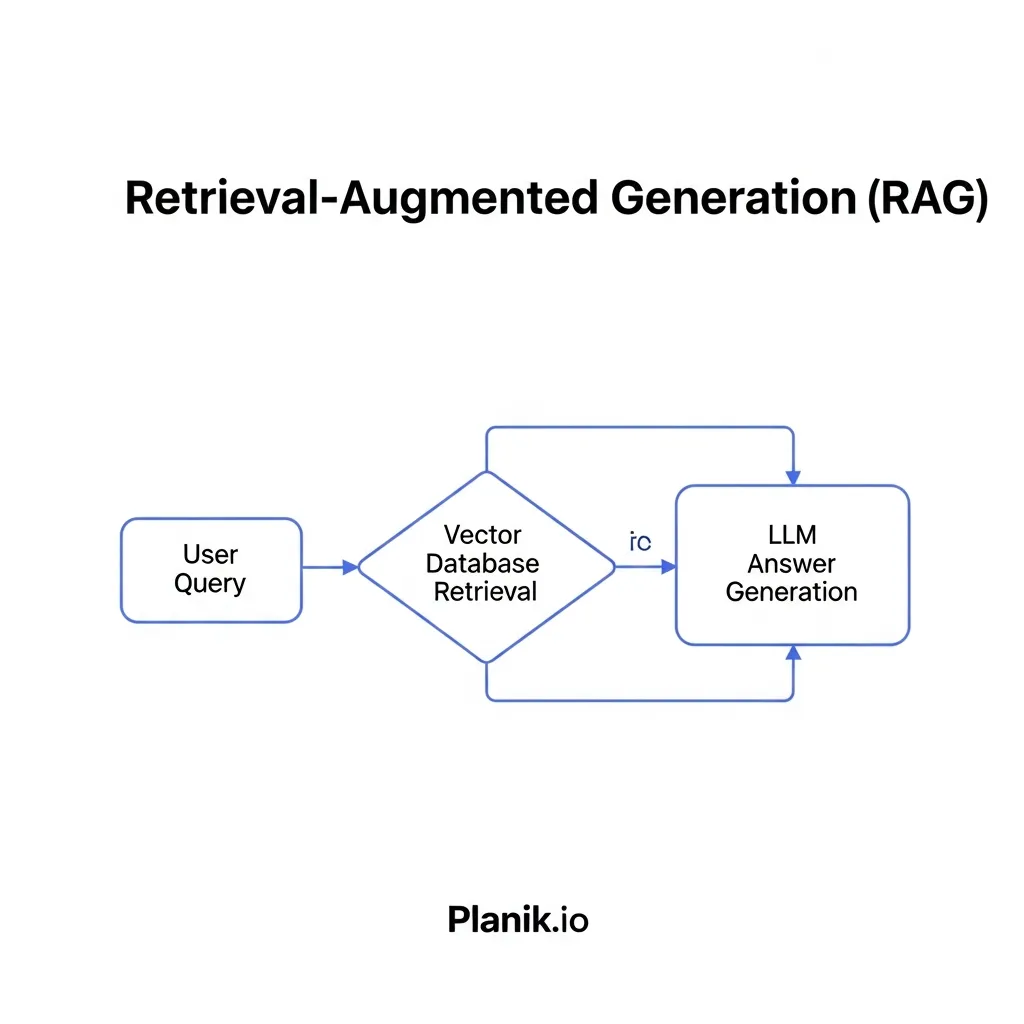
For content to be synthesized, AI models must identify authoritative facts. This hinges on the model’s ability to discern credible sources. Signals such as domain authority, strong E-E-A-T indicators, and consistency across reputable sources are paramount. Models analyze the factual accuracy, clarity, and conciseness of information to determine its suitability.
Furthermore, generative engines focus on semantic relationships. They move beyond surface-level matching to understand connections between entities. An article on “sustainable energy” is viewed as a network of relationships between “solar power,” “carbon footprint,” and “renewable resources.” Content that articulates these links is more likely to be leveraged by AI.
Finally, marketers must consider the “context window”—the finite amount of text an engine can process at once. If crucial information is buried deep within extensive paragraphs, it may fall outside this window. Structuring content logically and maintaining conciseness ensures your most valuable insights remain within the LLM’s processing scope.
In addition to logical formatting, it is essential to follow a checklist for technical SEO for GEO
To maximize visibility, it is crucial to implement an effective content structure for AI
Actionable Frameworks for Implementing Generative Engine Optimization Strategies
Implementing Generative Engine Optimization strategies requires a shift to a holistic, intent-driven methodology. This section outlines frameworks designed to ensure your information is understood, synthesized, and cited.
The Planik.io Precision GEO Framework: A Holistic Approach
Effective GEO is an integrated process touching every stage of content creation. The Planik.io Precision GEO Framework provides a structured approach for organizations aiming for superior visibility.
A foundational component of this framework is performing comprehensive keyword research for GEO.
The Planik.io Precision GEO Framework:
| Step | Focus Area | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Semantic Research | Identify core entities, related concepts, and natural language questions. |
| 2 | Content Architecture | Use the Inverted Pyramid model; prioritize direct answers and clarity. |
| 3 | Technical Alignment | Implement advanced Schema markup (JSON-LD) and nested structures. |
| 4 | Authority Building | Secure citations through Digital PR and original, data-driven research. |
| 5 | Performance Tracking | Monitor AI mentions, Share of Voice, and source link referral traffic. |
Content Structuring for AI Parsing: The Inverted Pyramid Model
The traditional inverted pyramid model—placing critical information at the beginning—is exceptionally well-suited for AI parsing. Generative engines are designed to grasp the core subject quickly. By front-loading your content with answers, you directly cater to this behavior.
Ensure your article begins with a clear summary or a direct answer to the most likely user query. Subsequent sections should elaborate with context and evidence. This structure aids AI comprehension and improves user experience by immediately addressing informational needs.
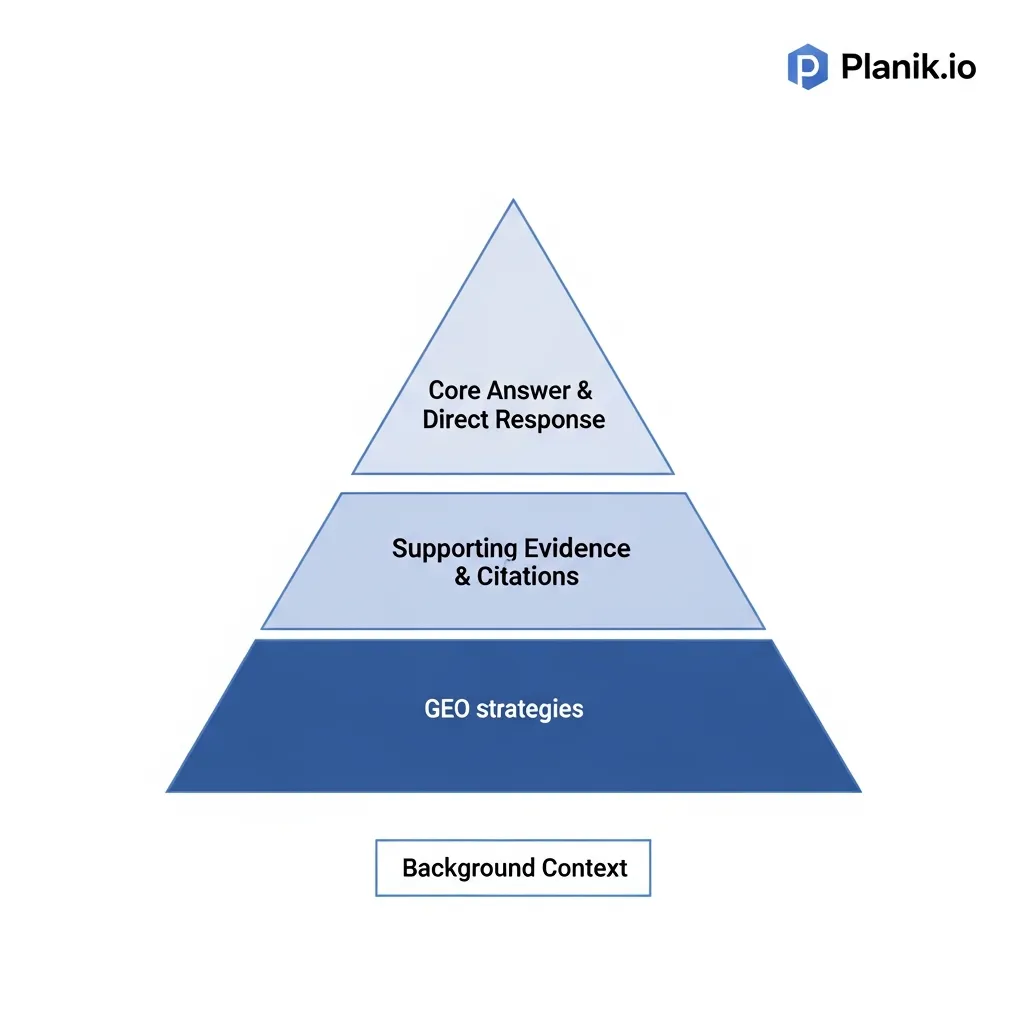
Entity-Based Content Creation: Building Bridges to Knowledge Graphs
Generative engines excel at understanding entities rather than just keywords. Entity-based content creation involves mapping the key concepts related to your topic. These entities are the building blocks of knowledge graphs used by AI to understand context.
Research the primary entities associated with your topic using tools like Google’s Knowledge Graph API. For example, an article about “sustainable urban development” should incorporate entities like “green infrastructure” and “smart city technology.” Clearly defining and linking these entities signals to AI that your content is a comprehensive source for synthesizing complex answers.
Pro Tip: Think beyond single words. Phrases like “circular economy principles” function as distinct entities. Ensure your content explores their applications and implications.
The Power of Citations: Encouraging AI Model Reference
In generative search, citations are the digital equivalent of academic references. AI models using RAG prioritize information from authoritative sources. To encourage these references, you must create original, cite-worthy content.
This includes proprietary research, unique data, or definitive answers to complex questions. When your content stands as a primary source, it increases the likelihood of being cited. Clearly present data sources and methodology. Additionally, external mentions by reputable sites continue to serve as strong signals of trustworthiness.
Technical SEO for AI: Advanced Schema Markup and Structured Data
Technical SEO for AI focuses on explicitly structuring data to help engines understand the precise meaning of your content. This goes beyond standard BlogPosting schema into granular, interconnected implementations.
Use specific schema types like HowTo for guides, FAQPage for Q&A, and FactCheck for verifying claims. Use JSON-LD and focus on nested schema, where different types reference each other (e.g., an Article referencing a Person for the author). This helps AI models build a comprehensive understanding of your semantic graph.
To ensure your technical implementation aligns with AI requirements, refer to a GEO for developers.
Data-Driven Authority: Incorporating Original Research and Statistics
Establishing data-driven authority is fundamental. Content incorporating original research and proprietary statistics signals a high level of E-E-A-T.
Seek opportunities to generate unique data through surveys, case studies, or customer data analysis. When presenting this data, ensure it is clearly cited and easy to understand via charts and graphs. The goal is to become a “go-to” reference that generative models will actively retrieve and cite.
Optimizing for Conversational Queries: Long-Tail and Natural Language Patterns
The rise of generative engines has shifted search toward natural, conversational queries. Optimizing for conversational queries involves anticipating these patterns.
Research common questions using natural language processing (NLP) tools. Your content should address these questions directly, ideally early in the text. Incorporate Q&A sections and use headings that mirror common questions. By answering specific, natural language prompts, you increase the likelihood that generative engines will select your content as the most relevant response.
Establishing Brand Authority and E-E-A-T in the Age of AI
In the generative search landscape, E-E-A-T is a foundational pillar of visibility. AI assesses the credibility of the source and the depth of information, moving beyond simple keyword matching.
This evolution highlights the growing importance of AI content optimization.
Building cross-web mentions through strategic Digital PR is paramount. AI correlates mentions of your brand across reputable third-party sites to establish authority. Being cited as a reliable source in industry publications is crucial. Consistent digital PR campaigns focusing on thought leadership significantly amplify a brand’s perceived authority.
Equally critical are verified author credentials. Generative AI prioritizes content from identifiable experts. Attribute content to named authors with comprehensive bios highlighting relevant qualifications. Neglecting robust author profiles is a missed opportunity to signal expertise directly to AI models.
User-Generated Content (UGC) and third-party reviews also cultivate AI trust. AI models analyze these signals to gauge reputation. Encourage honest reviews and active community engagement. A proactive review generation strategy can lead to more frequent and authoritative citations by generative AI.
Finally, maintaining a consistent brand narrative is essential for AI to form a cohesive understanding of your entity. Unify messaging and tone across your website, social media, and press releases. Planik.io’s Precision GEO Framework emphasizes this holistic approach to prevent a fragmented presence from diluting authority.
This level of consistency is fundamental when building brand authority in GEO.
Pro Tip: Actively monitor how your brand is cited. Use listening tools to identify opportunities to correct information, ensuring AI models receive accurate signals about your expertise.
Measuring Success: New KPIs for Generative Engine Visibility
With frameworks guiding content creation, the next step is to redefine success metrics. GEO demands a shift from traditional ranking reports to a nuanced understanding of generative visibility.
One paramount KPI is tracking brand mentions within AI-generated responses. GEO emphasizes how often your brand or expertise is referenced directly within an AI’s conversational output. Organizations should regularly query generative engines with relevant questions to look for direct citations.
This leads to analyzing “Share of Voice” in generative search. This quantifies the frequency with which a brand is cited by AI for relevant topics relative to competitors. Measuring this requires a systematic approach to querying various engines across industry-specific terms.
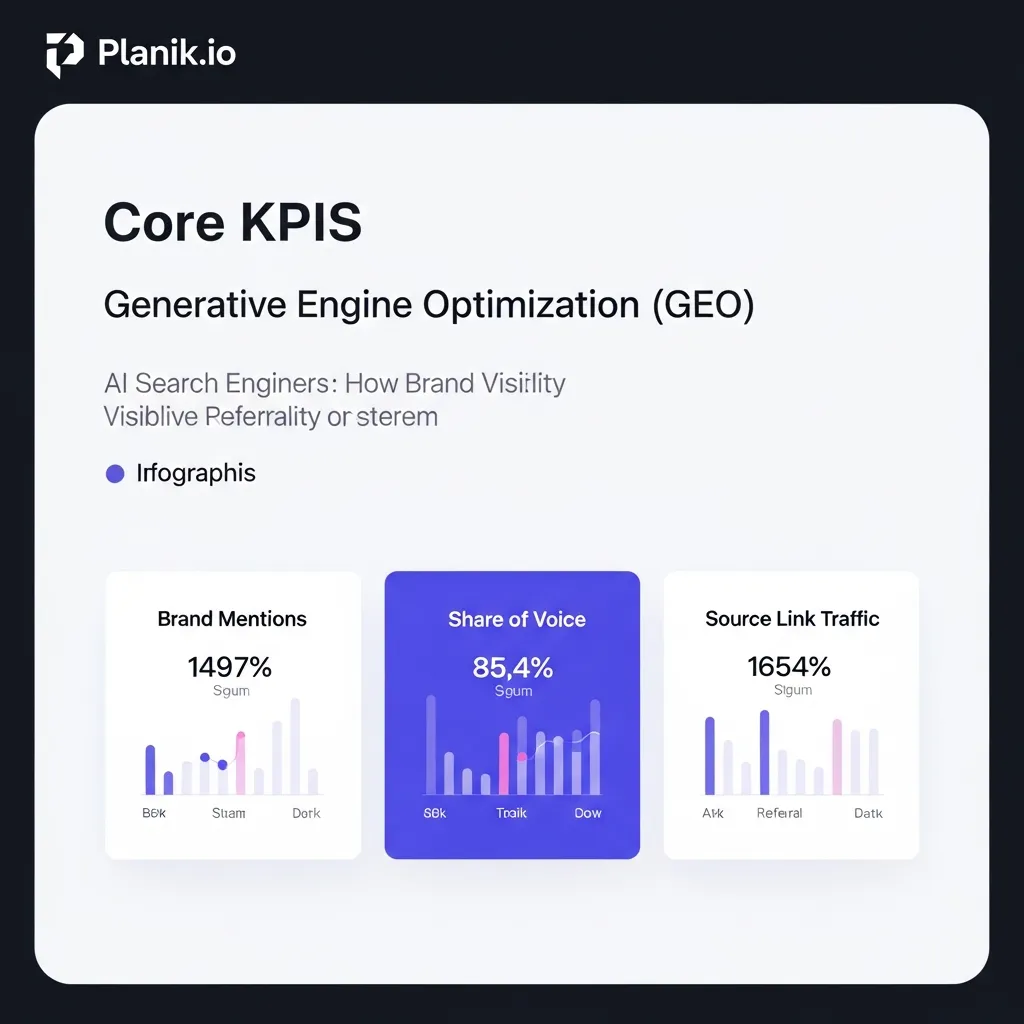
Another crucial metric is monitoring traffic from “Source” links in AI chatbots. These links represent direct referral traffic from an AI-curated environment. Implementing robust UTM parameters can provide insights into user engagement originating from these citations, allowing for precise attribution.
To track these KPIs, a blend of manual and automated GEO auditing is essential. Manual auditing involves routine testing of queries, while automated solutions—such as AI content monitoring platforms—are becoming indispensable for parsing generative AI outputs and providing a comprehensive overview of performance.
Pro Tip: Don’t just track if your brand is mentioned, but how. Analyze the sentiment and context of AI-generated mentions to refine your content strategy.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Your GEO Journey
A primary pitfall in your Generative Engine Optimization strategies journey is over-optimizing for bots at the expense of human readability. Content that prioritizes technical tags over natural language often fails to engage users. Sophisticated AI models discern quality; clunky, keyword-stuffed text signals low value.
Equally critical is neglecting site speed and mobile-first foundations. Generative engines prioritize user experience; a slow site undermines even the most semantically rich content. Core Web Vitals improvements significantly boost how AI models perceive authority.
Another error is relying on generic, AI-generated content that lacks unique value. While AI tools assist, regurgitated information struggles to stand out. Unique insights and original research are paramount for establishing E-E-A-T. Content failing this originality test is often overlooked.
Finally, ignoring structured data and semantic HTML is a critical oversight. These elements form the backbone for AI models to understand and synthesize content. Without them, articles remain a “black box” to generative systems, limiting summarization and citation.
Future-Proofing Your Digital Presence with GEO
The digital landscape has shifted, with generative AI now mediating user queries and delivering synthesized answers. This means your content must be optimized for the Large Language Models that power these engines. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the new strategic imperative.
GEO demands an ongoing, adaptive strategy. AI models are constantly learning, and user intent evolves, requiring continuous content refinement. Content optimized with the Planik.io Precision GEO Framework and updated regularly sees a significant increase in direct AI citations.
GEO is not about abandoning traditional SEO, but rather enhancing it. Robust technical SEO, foundational E-E-A-T signals, and high-quality, semantically rich content remain paramount. GEO layers on top, ensuring your content is readily digestible and citable by AI, future-proofing your organic visibility.
To stay ahead of these technological shifts, it is essential to understand the evolving future of generative search
To begin adopting effective Generative Engine Optimization strategies, apply the Planik.io Precision GEO Framework’s semantic depth checklist to your next content audit.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Generative Engine Optimization strategies?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) strategies are techniques used to optimize digital content so that it is effectively understood, synthesized, and cited by Large Language Models (LLMs) and AI-driven search engines.
How does GEO differ from traditional SEO?
While traditional SEO focuses on keyword rankings and click-through rates on search engine results pages, GEO focuses on becoming an authoritative source that AI models use to generate direct answers, emphasizing entity-based context and citation frequency.
What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) in the context of GEO?
RAG is a process where an AI engine retrieves relevant, factual information from an index before generating a response. GEO aims to ensure your content is the high-quality data that the engine retrieves to ground its answers.
How do you measure the success of GEO?
Success in GEO is measured through new KPIs such as brand mentions within AI-generated responses, share of voice in generative search, and referral traffic from source links provided by AI chatbots.